Welcome to the DermacenterMD Blog
Posts for category: Skin Cancer
 A good reminder from the Skin Cancer Foundation. It's important to remember that your family's medical history is crucial to your health.
A good reminder from the Skin Cancer Foundation. It's important to remember that your family's medical history is crucial to your health.
So you're sitting in the dermatologist's waiting room, filling out the usual forms required for a doctor visit. After filling in the basics, you spot the next question and realize you're stumped: it's asking about your family's medical history. Has anyone in your family had melanoma or any other form of skin cancer? Here's why the doctor asks, and what you need to know:
History Could Repeat Itself
A family history of melanoma increases your risk of developing the cancer yourself, according to Ramzi Saad, MD, a board-certified dermatologist and Skin Cancer Foundation member based in Plymouth, Massachusetts. In fact, about one in every 10 patients diagnosed with melanoma has a family member with a history of the disease. When gathering family history, Dr. Saad says, the more information, the better.
"We ask for a history of skin cancers, specifically melanoma, but getting a family history of all cancers is also important," he says. "There are some genetic connections between melanoma and other cancers."
Closer Relative, Higher Risk
Gathering accurate information about multiple family members can be a little intimidating, but Dr. Saad notes a few points that are of particular importance when digging through medical history. The number of relatives that have had melanoma, particularly first-degree relatives like parents or siblings, is a definite need-to-know. Each person with a first-degree relative diagnosed with melanoma has a whopping 50 percent greater chance of developing the disease than people who do not have a family history of the disease.
Saad says the more complete the history, the better, but the number of first-degree relatives with the disease is the most important predictive factor for an increased risk of melanoma.
Take Action
What happens if you do find out that skin cancer runs in your family? Saad recommends extra vigilance for prevention, being sure to use sunscreen every day and avoiding unnecessary sun exposure. He points to our tips on how to perform a self exam, but notes that seeing a dermatologist annually is critical as well.
“A full skin examination by a trained professional can help to identify suspicious lesions needing removal,” Dr. Saad says. A board-certified dermatologist will also be able to help patients keep an eye on lesions that may become cancerous in the future, and establish the appropriate follow-up frequency for that individual’s skin checks.
So in advance of your next skin check, try gathering some info on your family’s medical history. You might be surprised to learn that someone close to you once dealt with skin cancer, and that knowledge can help your dermatologist help you.
For more information about skin cancer see the Skin Cancer Foundations blog: http://blog.skincancer.org/2017/02/22/what-you-should-know-about-your-familys-history-of-melanoma/
If you or someone you know should have their skin checked, give us a call today at 574-522-0265 to schedule an appointment.
 Check out this article from the Skin Cancer Foundation. It's important to remember that people of all skin types and tones can be affected by skin cancer.
Check out this article from the Skin Cancer Foundation. It's important to remember that people of all skin types and tones can be affected by skin cancer.
People who have dark skin tones often believe they're not at risk for skin cancer, but that is a dangerous misconception , says dermatologist Maritza I. Perez, MD, a senior vice president of The Skin Cancer Foundation.
"Anyone can get skin cancer, regardless of race," she says. While incidence of melanoma is higher in the Caucasian population, a July 2016 study in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology showed it is more deadly in people of color. African American patients were most likely to be diagnosed with melanoma in its later stages than any other group in the stuy, and they also had the worst prognosis and the lowerst overall survival rate. Most skin cancers are associated with ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or from tanning beds, says Dr. Perez. Yes, darker skin produces more of the pigment called melanin that does help protect skin- but onlyto a certain extent. People of color can still get sunburned, and they can also develop skin cancer from UV damage.
It’s of concern that 65 percent of African American participants in a survey said they never used sunscreen. This needs to change, says Dr. Perez. “Remember, ethnicity does not define skin type. It can represent a wide range of skin tones with a wide range of risks.” To avoid premature aging and damage that can lead to skin cancer, everyone should use sunscreen every day and practice sun-safe habits, such as seeking shade and wearing protective clothing, hats and UV-blocking sunglasses.
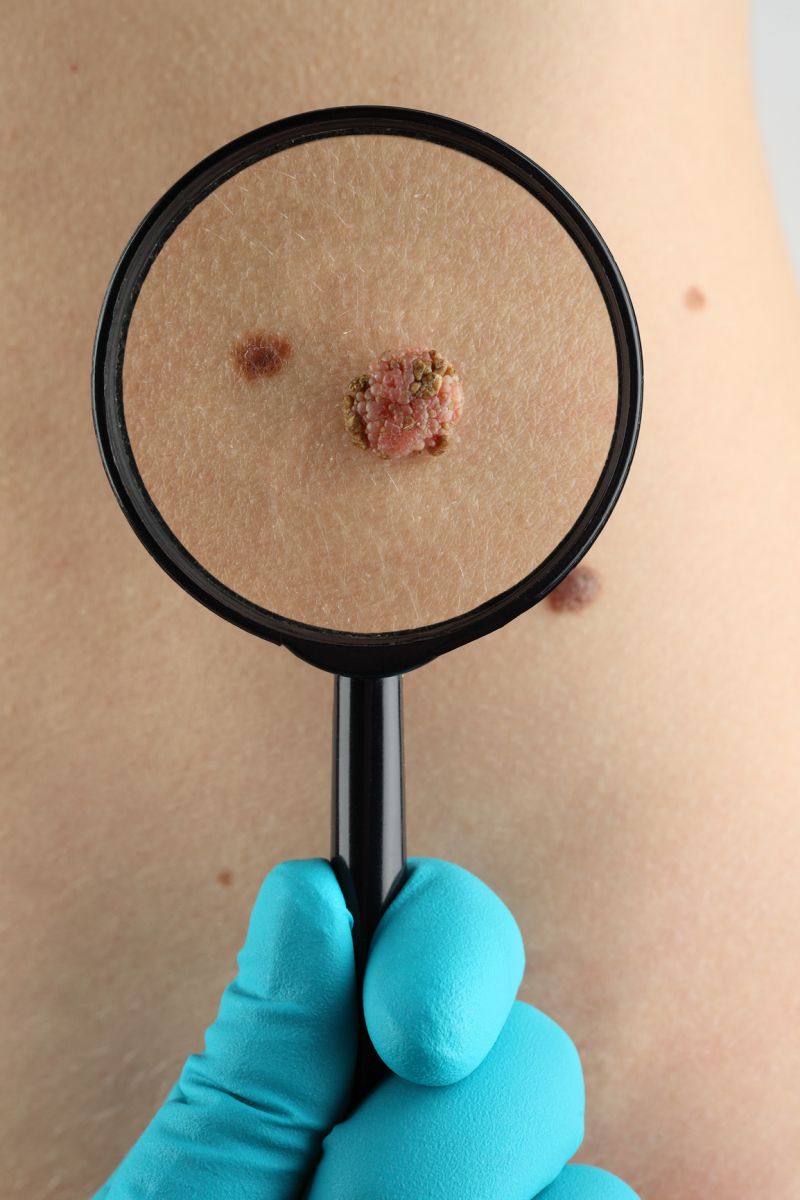
Additionally, certain skin cancers are caused by factors other than UV — such as genetics or environmental influences — and may occur on parts of the body rarely exposed to the sun. For example, people who have dark skin are more susceptible to acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM), an especially dangerous form of melanoma that typically appears on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. (The Jamaican singer and musician Bob Marley died of ALM when he was only 36.)


People who have dark skin are more susceptible to acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM), like these examples above.
It’s crucial to detect skin cancer early, when it is easiest to treat and most likely to be cured. Dr. Perez says she advises people of all ethnicities to do a monthly skin self-exam and see a dermatologist annually — and sooner if any of the warning signs appear:
- A bump, patch, sore or growth that bleeds, oozes, crusts, doesn’t heal or lasts longer than a month. This may indicate basal cell carcinoma.
- An ulcer, scaly red patch, wart-like growth or sore that sometimes crusts or bleeds could be a sign of squamous cell carcinoma. This type of skin cancer can also develop in old scars or areas of previous physical trauma or inflammation.
- New or existing moles that are asymmetrical, have an irregular border, more than one color, are larger than a pencil eraser or change in any way may indicate melanoma. Pay special attention to suspicious spots on the hands, soles of the feet or under the nails, which could signify ALM.
 Adults who use sunscreen daily can drastically reduce their risk of developing melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, according to recent landmark research from Australia. Researchers found that daily application of an SPF 16 sunscreen to the head, neck, arms, and hands reduced melanoma incidence by half in study participants.
Adults who use sunscreen daily can drastically reduce their risk of developing melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, according to recent landmark research from Australia. Researchers found that daily application of an SPF 16 sunscreen to the head, neck, arms, and hands reduced melanoma incidence by half in study participants.
In the Australian study, led by epidemiologist Adele Green, MD, University of Queensland, more than 1,600 white Australian adults between age 25 and 65 were studied for more than a decade. The subjects were divided into two groups, one told to continue using (or not using) sunscreen as they always had, the other given careful instruction in proper daily sunscreen application. The subjects were monitored closely through daily self-reports of sunscreen use, as well as collection and examination of all the sunscreen containers they had used. Only 11 melanomas developed in the daily sunscreen users, vs. 22 in the control group, a 50 percent reduction. In addition, invasive melanomas (tumors that penetrate beyond the skin surface) were reduced by 73 percent (3 tumors vs. 11) and average thickness by more than half a millimeter in the daily sunscreen group.
The trial's findings are the first to provide strong direct evidence for a reduction in the incidence of invasive melanoma after regular application of broad-spectrum sunscreen in adults. The scientists acknowledge that the study was relatively small and needs to be reinforced by further research, but consider their results convincing enough to recommend daily sunscreen application, along with "other standard sun protection measures like avoiding midday sun and use of protective clothing."
From: The Skin Cancer Foundation
Source: www.skincancer.org
 An article from the Skin Cancer Foundation.
An article from the Skin Cancer Foundation.
Source: www.skincancer.org
People who have had the nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSCs) basal and squamous cell carcinoma (BCC and SCC) are approximately twice as likely as other people to develop non-skin cancers, according to a study in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
The findings are of particular concern because NMSC is the world's most common malignancy, with over a million cases diagnosed every year in the US alone. Currently, it's estimated that one in five Americans will develop NMSC at some point in their lives. About 90 percent of these cancers are associated with exposure to the sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation. While NMSCs have very high cure rates when caught early, they should not be taken lightly, as this study shows.
Researchers led by Anthony J. Alberg, PhD, of the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, studied demographic and health information from 19,174 patients in the Maryland-based CLUE (Give us a Clue to Cancer and Heart Disease) II study, from 1989 though 2005. Some 769 patients in the study were diagnosed with NMSC, and by the end of 2005, 181 of these patients, or about 23 percent, had developed another form of (non-skin-related, or noncutaneous) cancer. In contrast, only about 12 percent of people (2156 of 18,405) who did not have NMSC were subsequently diagnosed with a noncutaneous cancer. Researchers took variables such as cigarette smoking and skin type (susceptibility to sunburn and blistering) into account. Nonetheless, those with NMSC had about twice the risk of developing noncutaneous cancers as those who did not have NMSC. Researchers also found that the earlier the age at diagnosis of NMSC, the more likely participants were to develop noncutaneous cancers.
The full implications of this research are not yet known, but while nonmelanoma skin cancers are rarely life-threatening, they can be highly disfiguring if not caught early, and it is well known that having a history of NMSC means you are also at increased risk of developing melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, which claims more than 8200 lives a year in the US. If you have had an NMSC, you are at higher risk of developing not only future NMSCs and melanomas, but also other, potentially dangerous cancers. Routine screening for both skin cancers and non-skin cancers is thus advisable.
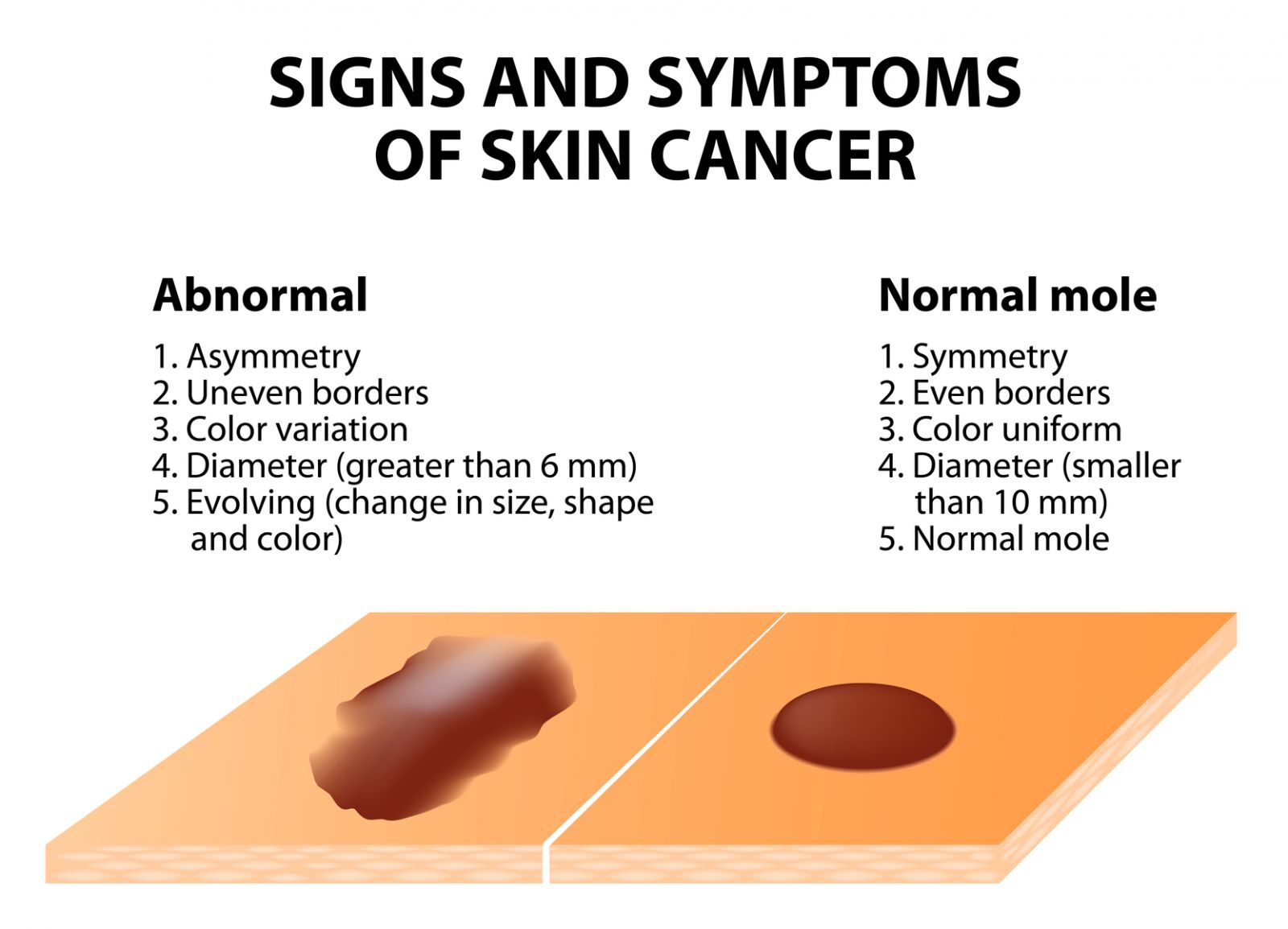
 Q: "I understand you need to keep an eye on moles on your skin to guard against the risk of skin cancer, but what exactly should I be looking for?"
Q: "I understand you need to keep an eye on moles on your skin to guard against the risk of skin cancer, but what exactly should I be looking for?"
A: Moles are clumps of clustered pigment cells that are nearly always darker than freckles. All changes in existing moles should be checked by your doctor. Any that cause concern will be removed and sent off for analysis. You should also check moles yourself once a month. Try the following A, B, C, D. and E Code: check for A (asymmetry); B (border irregularity); C (color change); D (large diameter), and E (evolution or change).
A mole or a dark freckle spot can turn to cancer or melanoma without symptoms such as itching, burning, or pain. So if you have a mole which is dark, irregular or changing then please do get it evaluated. It is estimated that 1 in 75 Americans will have melanoma at some point in their life. This deadly cancer can be relatively easily treated if caught early.
Call our office today at 574-522-0265 to set up an appointment with one of our highly trained providers.
Archive:
Tags
- dry skin (2)
- moisturizer (1)
- sensitive skin (3)
- PA (2)
- Skincare (2)
- skin cancer (29)
- cancer (6)
- facts (1)
- skin (19)
- dermatology (22)
- skin care (19)
- cosmetic (2)
- wrinkles (1)
- Botox (4)
- Dysport (3)
- sleep (1)
- look good (1)
- daily routine (1)
- healthy lifestyle (1)
- doctor (2)
- patient (1)
- sun protection (5)
- sunscreen (14)
- aging dermatology (1)
- providers (1)
- tanning (2)
- sun (6)
- UVA rays (2)
- UVB rays (2)
- melanoma (10)
- Acne (2)
- Treatment (2)
- sunscren (1)
- sun exposure (5)
- Melanoma Monday (2)
- Skin Cancer Awareness Month (1)
- education (2)
- skin cancer specialist (1)
- basal cell carcinoma (1)
- squamous cell carcinoma (1)
- ingredients (2)
- improve your smile (1)
- cosmetics (1)
- laser (1)
- fillers (2)
- sunburn (3)
- avoid the sun (1)
- hat (1)
- sun clothing (1)
- SPF (1)
- Rosacea (3)
- NP (1)
- Nurse Practitioner (1)
- mid-level provider (1)
- physician (1)
- dermatologist (6)
- cosmetic dermatology (4)
- anti-aging (2)
- youthful looks (1)
- Eczema (2)
- rash (2)
- itch (1)
- the rash that itches (1)
- reduce itch (1)
- itching (1)
- getting along with others (1)
- basal cell (2)
- squamous cell (2)
- detection (1)
- Mohs surgery (2)
- photoaging (1)
- Inspiring (1)
- word of the day (1)
- inspiration (3)
- uplifting (1)
- protection (4)
- lips (1)
- reduce wrinkles (1)
- look younger (1)
- encouragement (1)
- never give up (1)
- you can do it (1)
- medical school (1)
- dreams (1)
- brown spots (1)
- moles (2)
- liver spots (1)
- age spots (1)
- Abe Lincoln (1)
- life lessons (1)
- lip cancer (1)
- health (12)
- motivation (1)
- work (1)
- people (2)
- home life (1)
- lifestyle (1)
- ABCDEs of Melanoma (1)
- mole (1)
- skin check (2)
- skin facts (2)
- odd (1)
- fun (1)
- interesting (1)
- lung cancer (1)
- disease (1)
- Christmas (2)
- gifts (1)
- sun burn (1)
- winter skin tips (1)
- itchy skin (1)
- winter skin (1)
- myths (1)
- myth busted (1)
- skin protection (1)
- sunscreen safety (1)
- specialist (1)
- red skin (1)
- irritation (1)
- feel good (1)
- helping (1)
- help (1)
- helping others (1)
- treatment options (1)
- skin health (9)
- Vitamin D (2)
- tanning beds (1)
- skin health. dermatology (1)
- sunshine (1)
- awareness (1)
- prevention (1)
- sun damage (3)
- connections (1)
- working together (1)
- health care (1)
- biotin (1)
- medical (1)
- aging (1)
- elkhart (1)
- Roger Moore (1)
- check (1)
- skin type (1)
- skin cancer prevention (1)
- gift guide (1)
- Christmas gift guide (1)
- Dr. Roger Moore (1)
- holidays (1)
- family history (1)
