Welcome to the DermacenterMD Blog
Posts for tag: cancer
 Check out this article from the Skin Cancer Foundation. It's important to remember that people of all skin types and tones can be affected by skin cancer.
Check out this article from the Skin Cancer Foundation. It's important to remember that people of all skin types and tones can be affected by skin cancer.
People who have dark skin tones often believe they're not at risk for skin cancer, but that is a dangerous misconception , says dermatologist Maritza I. Perez, MD, a senior vice president of The Skin Cancer Foundation.
"Anyone can get skin cancer, regardless of race," she says. While incidence of melanoma is higher in the Caucasian population, a July 2016 study in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology showed it is more deadly in people of color. African American patients were most likely to be diagnosed with melanoma in its later stages than any other group in the stuy, and they also had the worst prognosis and the lowerst overall survival rate. Most skin cancers are associated with ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or from tanning beds, says Dr. Perez. Yes, darker skin produces more of the pigment called melanin that does help protect skin- but onlyto a certain extent. People of color can still get sunburned, and they can also develop skin cancer from UV damage.
It’s of concern that 65 percent of African American participants in a survey said they never used sunscreen. This needs to change, says Dr. Perez. “Remember, ethnicity does not define skin type. It can represent a wide range of skin tones with a wide range of risks.” To avoid premature aging and damage that can lead to skin cancer, everyone should use sunscreen every day and practice sun-safe habits, such as seeking shade and wearing protective clothing, hats and UV-blocking sunglasses.
Additionally, certain skin cancers are caused by factors other than UV — such as genetics or environmental influences — and may occur on parts of the body rarely exposed to the sun. For example, people who have dark skin are more susceptible to acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM), an especially dangerous form of melanoma that typically appears on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. (The Jamaican singer and musician Bob Marley died of ALM when he was only 36.)


People who have dark skin are more susceptible to acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM), like these examples above.
It’s crucial to detect skin cancer early, when it is easiest to treat and most likely to be cured. Dr. Perez says she advises people of all ethnicities to do a monthly skin self-exam and see a dermatologist annually — and sooner if any of the warning signs appear:
- A bump, patch, sore or growth that bleeds, oozes, crusts, doesn’t heal or lasts longer than a month. This may indicate basal cell carcinoma.
- An ulcer, scaly red patch, wart-like growth or sore that sometimes crusts or bleeds could be a sign of squamous cell carcinoma. This type of skin cancer can also develop in old scars or areas of previous physical trauma or inflammation.
- New or existing moles that are asymmetrical, have an irregular border, more than one color, are larger than a pencil eraser or change in any way may indicate melanoma. Pay special attention to suspicious spots on the hands, soles of the feet or under the nails, which could signify ALM.
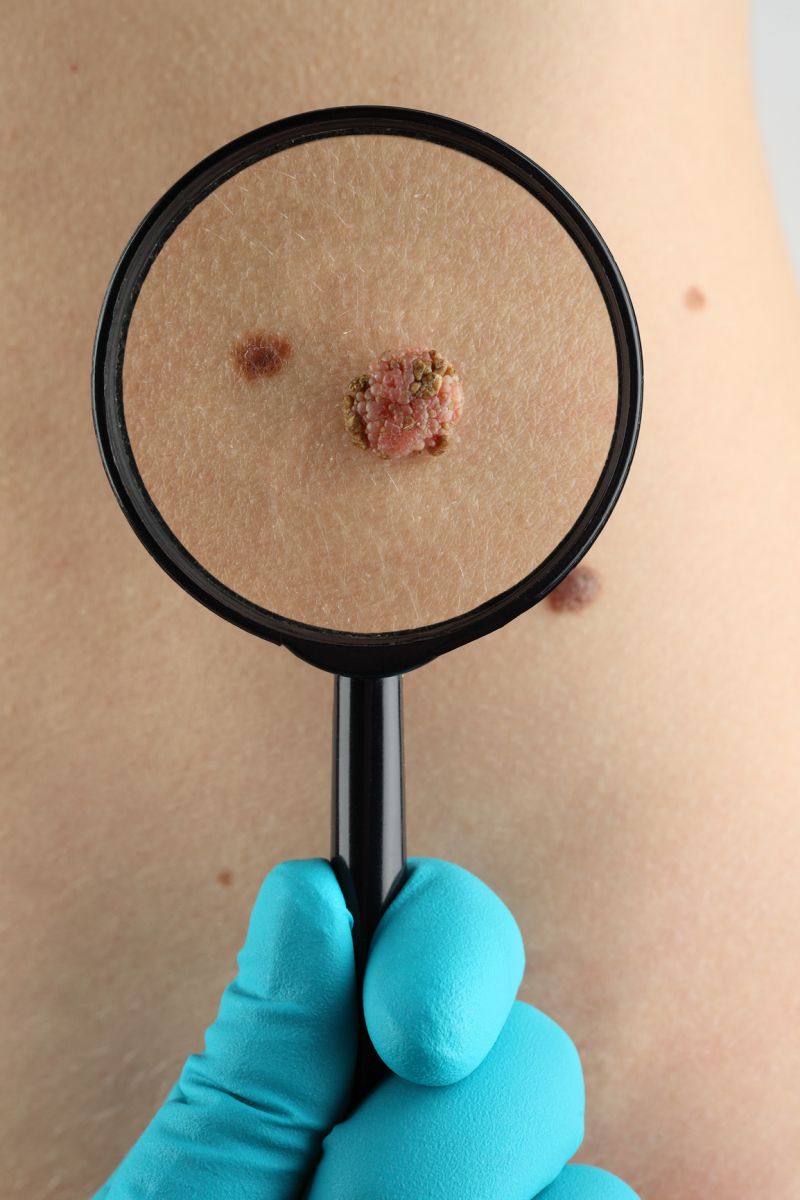 The answer is simple- YES. Check out the article below from the Skin Cancer Foundation on the importance of taking the time to check your own skin every month. It could save your life!
The answer is simple- YES. Check out the article below from the Skin Cancer Foundation on the importance of taking the time to check your own skin every month. It could save your life!
The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends that everyone practice monthly head-to-toe self examination of their skin, so that they can find any new or changing lesions that might be cancerous or precancerous. Skin cancers found and removed early are almost always curable. Learn about the warnings signs of skin cancer and what to look for during a self examination. If you spot anything suspicious, see a doctor.
Performed regularly, self examination can alert you to changes in your skin and aid in the early detection of skin cancer. It should be done often enough to become a habit, but not so often as to feel like a bother. For most people, once a month is ideal, but ask your doctor if you should do more frequent checks.
Find step-by-step instructions on how to perform a self-examination by clicking HERE.
You may find it helpful to have a doctor do a full-body exam first, to assure you that any existing spots, freckles, or moles are normal or treat any that may not be. After the first few times, self examination should take no more than 10 minutes – a small investment in what could be a life-saving procedure.
If you or someone you know has found a suspicious lesion, give our office a call to have it examined. We are accepting new patients.
DERMACENTERMD 574-522-0265
 Sunscreen is a must. It is essential that you protect your skin from the harmful rays of the sun. Taking the proper precautions when it comes to the sun can decrease signs of aging and reduce your chances of getting skin cancer. Below you will find the answers to common questions that you should know make a point to know and understand. Knowing what sunscreen is and how it works can help you in your efforts to protect your skin and keep yourself and the ones you love healthy.
Sunscreen is a must. It is essential that you protect your skin from the harmful rays of the sun. Taking the proper precautions when it comes to the sun can decrease signs of aging and reduce your chances of getting skin cancer. Below you will find the answers to common questions that you should know make a point to know and understand. Knowing what sunscreen is and how it works can help you in your efforts to protect your skin and keep yourself and the ones you love healthy.
Below are several common sunscreen questions with answers taken from the Skin Cancer Foundation:
What Are Sunscreens?
Sunscreens are products combining several ingredients that help prevent the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation from reaching the skin. Two types of ultraviolet radiation, UVA and UVB, damage the skin and increase your risk of skin cancer. Sunscreens vary in their ability to protect against UVA and UVB.
What Are UVA and UVB?
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is part of the electromagnetic (light) spectrum that reaches the earth from the sun. It has wavelengths shorter than visible light, making it invisible to the naked eye. Ultraviolet A (UVA) is the longer wave UV ray that causes lasting skin damage, skin aging, and can cause skin cancer. Ultraviolet B (UVB) is the shorter wave UV ray that causes sunburns, skin damage, and can cause skin cancer.
What Is SPF?
SPF – or Sun Protection Factor – is a measure of a sunscreen's ability to prevent UVB from damaging the skin. Here's how it works: If it takes 20 minutes for your unprotected skin to start turning red, using an SPF 15 sunscreen theoretically prevents reddening 15 times longer – about five hours. Most sunscreens with an SPF of 15 or higher do an excellent job of protecting against UVB.
What Does Broad-Spectrum Mean?
Broad-spectrum sunscreens protect the skin from both UVA and UVB rays. Beginning in December 2012, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) began to implement new rules for "broad-spectrum" products.
So, next time you head outside to enjoy the outdoors, don't forget your sunscreen!!
Source:
http://www.skincancer.org/prevention/sun-protection/sunscreen
 In dermatology, acceptance and responsibility are two key components that we need. Why? Well, I will tell you why.
In dermatology, acceptance and responsibility are two key components that we need. Why? Well, I will tell you why.
The lack of protection from the sun is one of the underlying driving forces to precancers (actinic keratosis), wrinkles, pigmentation, and even skin cancer. Unfortunately, most every person does not apply the amount of sun protection that they should. It’s essential that we wear sunscreen and protect ourselves. Even a scientific study done on farmers in west Texas backs this up. When sunscreen was applied to one half of the face and not the other half during three months of summer, the side of the face with sunscreen applied every day has half as many precancer (actinic keratosis) growths as the other side of the face.
This simple study demonstrated the power of daily sunscreen for reducing precancer lesions. On top of this, we know that age spots, wrinkles, and skin cancer are caused by sun exposure.
So, to get our skin looking and feeling the best, we need to use sunscreen every day. This can be in the form of lotions, sunscreens themselves, and make up for women. In addition, choosing a sunscreen that has the proper ingredients is key. Finding sunscreen with Titanium Dioxide or Zinc Oxide is useful since these ingredients are physical blockers. This means that they bounce the sun off the skin. Another quality ingredient in sunscreen is Avobenzone or Parsol 1789. This is also an excellent ingredient which can be a powerful agent in preventing sun damage.
Use daily sunscreen with Titanium Dioxide, Zinc Oxide or Avobenzone (Parsol 1789) to reduce your risk of sun damage and skin cancer. The simple habit could pay big dividends!
.jpg)
An article from The Skin Cancer Foundation
Source: www.skincancer.org
Published on January 29, 2014
JAMA Dermatology has released a study, “International Prevalence of Indoor Tanning -- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.”
Key study takeaways at-a-glance:
- The number of skin cancer cases due to tanning is higher than the number of lung cancer cases due to smoking.
- In the US alone, 419,254 cases of skin cancer can be attributed to indoor tanning. Out of this number, 6,199 are melanoma cases.
The Skin Cancer Foundation’s Position:
The study results demonstrate that tanning bed use, particularly among young people, is an alarmingly widespread behavior. In the US, 35% of adults and 55% of college students have tanned, and the study found there are more than 419,000 new skin cancer cases attributable to indoor tanning each year. Worldwide, there are more skin cancer cases due to indoor tanning than there are lung cancer cases due to smoking.
These results are not surprising given what we know about indoor tanning behaviors and society’s flawed view that an artificially tanned look is beautiful. The Foundation continually works to change perceptions about tanning through its public education efforts, including its PSA campaign Go With Your Own Glow, which is designed to encourage women to embrace and protect their natural skin tones.
The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends that people of all ages, genders, and ethnic backgrounds avoid indoor tanning and take precautions in the sun by limiting outdoor time between 10 am and 4 pm, seeking the shade when outdoors, using a broad spectrum SPF 15+ sunscreen (SPF 30+ sunscreen for extended stays outdoors), and wearing protective clothing, including wide-brimmed hats and UV-blocking sunglasses.
This is the first summary of the international prevalence of indoor tanning exposure. 88 records (studies) were included in the meta-analysis, and the results include data from 406,696 participants. Analyses were performed separately for three geographic regions: the United States and Canada, Northern and Western Europe and Australia, as well as for these regions combined.
Archive:
Tags
- dry skin (2)
- moisturizer (1)
- sensitive skin (3)
- PA (2)
- Skincare (2)
- skin cancer (29)
- cancer (6)
- facts (1)
- skin (19)
- dermatology (22)
- skin care (19)
- cosmetic (2)
- wrinkles (1)
- Botox (4)
- Dysport (3)
- sleep (1)
- look good (1)
- daily routine (1)
- healthy lifestyle (1)
- doctor (2)
- patient (1)
- sun protection (5)
- sunscreen (14)
- aging dermatology (1)
- providers (1)
- tanning (2)
- sun (6)
- UVA rays (2)
- UVB rays (2)
- melanoma (10)
- Acne (2)
- Treatment (2)
- sunscren (1)
- sun exposure (5)
- Melanoma Monday (2)
- Skin Cancer Awareness Month (1)
- education (2)
- skin cancer specialist (1)
- basal cell carcinoma (1)
- squamous cell carcinoma (1)
- ingredients (2)
- improve your smile (1)
- cosmetics (1)
- laser (1)
- fillers (2)
- sunburn (3)
- avoid the sun (1)
- hat (1)
- sun clothing (1)
- SPF (1)
- Rosacea (3)
- NP (1)
- Nurse Practitioner (1)
- mid-level provider (1)
- physician (1)
- dermatologist (6)
- cosmetic dermatology (4)
- anti-aging (2)
- youthful looks (1)
- Eczema (2)
- rash (2)
- itch (1)
- the rash that itches (1)
- reduce itch (1)
- itching (1)
- getting along with others (1)
- basal cell (2)
- squamous cell (2)
- detection (1)
- Mohs surgery (2)
- photoaging (1)
- Inspiring (1)
- word of the day (1)
- inspiration (3)
- uplifting (1)
- protection (4)
- lips (1)
- reduce wrinkles (1)
- look younger (1)
- encouragement (1)
- never give up (1)
- you can do it (1)
- medical school (1)
- dreams (1)
- brown spots (1)
- moles (2)
- liver spots (1)
- age spots (1)
- Abe Lincoln (1)
- life lessons (1)
- lip cancer (1)
- health (12)
- motivation (1)
- work (1)
- people (2)
- home life (1)
- lifestyle (1)
- ABCDEs of Melanoma (1)
- mole (1)
- skin check (2)
- skin facts (2)
- odd (1)
- fun (1)
- interesting (1)
- lung cancer (1)
- disease (1)
- Christmas (2)
- gifts (1)
- sun burn (1)
- winter skin tips (1)
- itchy skin (1)
- winter skin (1)
- myths (1)
- myth busted (1)
- skin protection (1)
- sunscreen safety (1)
- specialist (1)
- red skin (1)
- irritation (1)
- feel good (1)
- helping (1)
- help (1)
- helping others (1)
- treatment options (1)
- skin health (9)
- Vitamin D (2)
- tanning beds (1)
- skin health. dermatology (1)
- sunshine (1)
- awareness (1)
- prevention (1)
- sun damage (3)
- connections (1)
- working together (1)
- health care (1)
- biotin (1)
- medical (1)
- aging (1)
- elkhart (1)
- Roger Moore (1)
- check (1)
- skin type (1)
- skin cancer prevention (1)
- gift guide (1)
- Christmas gift guide (1)
- Dr. Roger Moore (1)
- holidays (1)
- family history (1)
